Update GPU Drivers in 2026 | Complete Guide for All Windows Versions
When GPU drivers are outdated, the operating system cannot communicate properly with the graphics card. As a result, several issues may occur, including game crashes and incorrect rendering of text, images, or videos. So, keeping GPU drivers updated ensures stable performance, compatibility, and visual accuracy. You can instantly update GPU drivers using simple methods such as Device Manager, Windows Update, or downloading the latest drivers directly from the official websites of NVIDIA, Intel, and AMD.
A GPU driver is system-level software that tells the GPU how to render graphical data for Windows applications. It works closely with core graphics technologies such as DirectX, which handles most Windows games and multimedia applications; OpenGL, which is widely used in cross-platform and professional software; and Vulkan, a low-level graphics API designed for high-performance and resource-efficient rendering. These technologies act as a bridge between applications and the GPU, allowing graphics tasks to be processed efficiently.
Without a proper GPU driver, the graphics card can only provide basic display output, while advanced features like hardware acceleration and high refresh rate support remain disabled. Once your drivers are up to date, you can experience better gaming performance, fixes for graphical glitches and display errors, improved rendering quality, enhanced compatibility with modern applications, and access to new features and performance optimizations.
How to Update GPU Drivers Using Device Manager?
Device Manager is a built-in Windows hardware management tool that allows users to manually update graphics drivers for NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel GPUs. Windows will search for the latest Microsoft-certified (WHQL) driver and install it if available. After installation, a system restart is recommended.
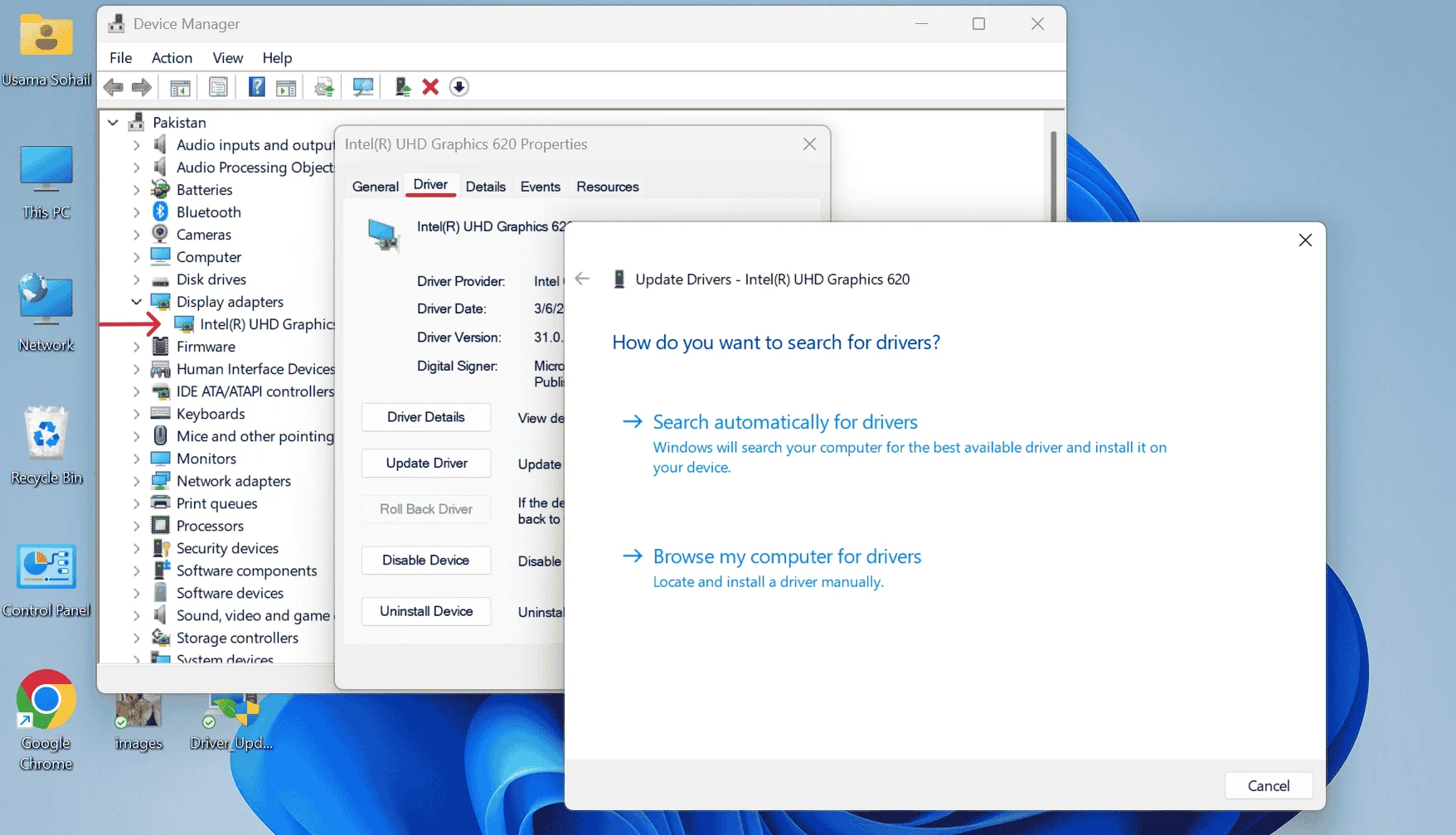
If you have already downloaded the driver from the manufacturer’s website (NVIDIA, AMD, or Intel), you can choose “Browse my computer for driver software” instead.
Steps:
How to Update GPU Drivers Using Windows Update?
For Windows 10 and 11, Windows Update is Microsoft’s built-in system that updates both the OS and graphics drivers automatically. But in older versions like Windows 7 or 8, GPU drivers may appear under the Optional Updates section, where you can manually select and install them.
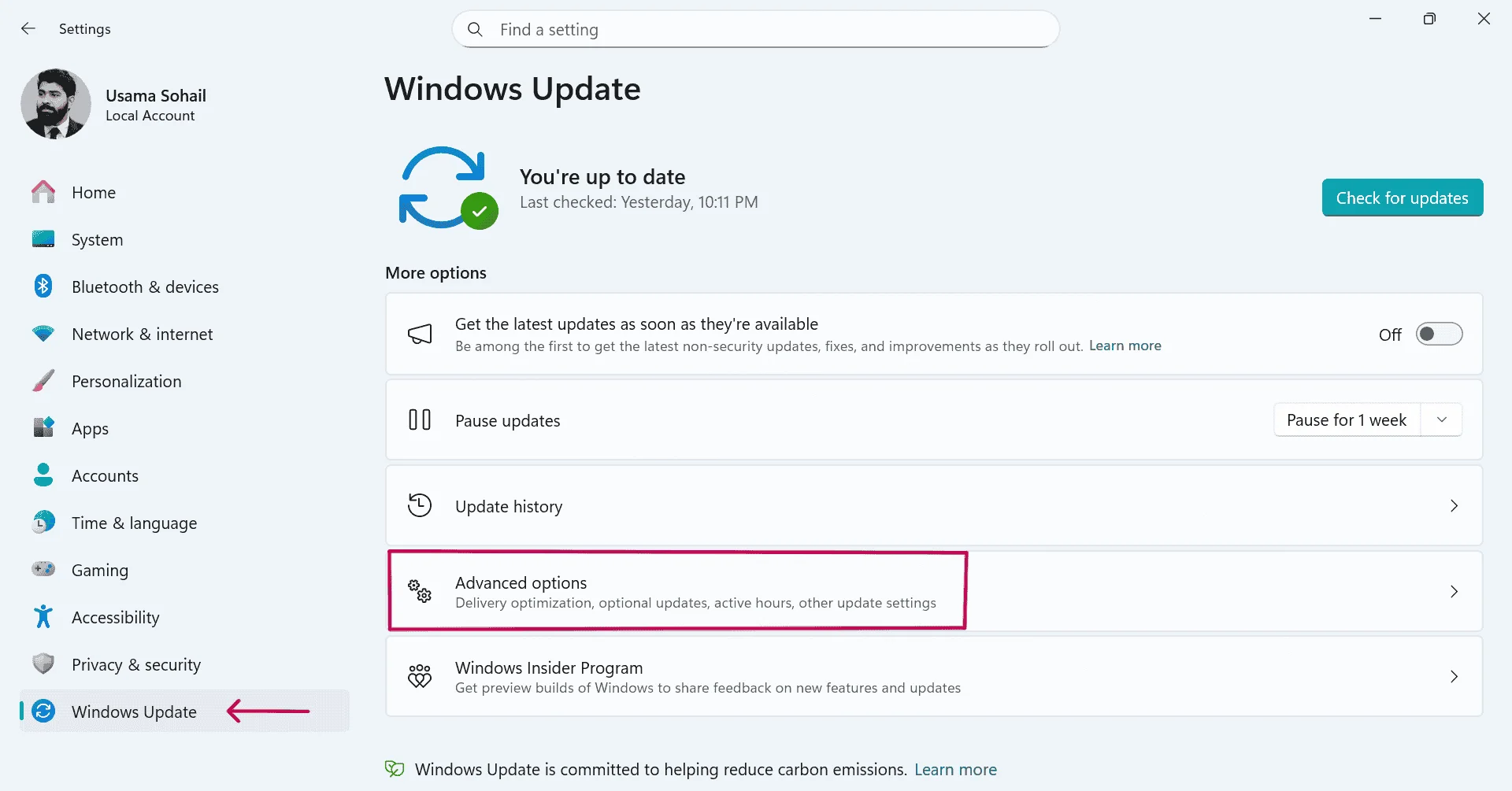
⮞ Windows 11
To update GPU drivers on Windows 11, open Start Menu → Settings → Windows Update → Advanced options → Optional updates → Driver updates, select the available GPU driver (NVIDIA / AMD / Intel), and click Download & install. Restart the system if prompted.
⮞ Windows 10
On Windows 10, go to Start Menu → Settings → Update & Security → Windows Update, then click Check for updates. If a compatible GPU driver is available, Windows will install it automatically. In some builds, graphics drivers may appear under View optional updates → Driver updates. Restart the system if required.
⮞ Windows 8 / 8.1
For Windows 8 or 8.1, navigate to Start Screen → Control Panel → System and Security → Windows Update, click Check for updates, open Optional updates, select the available graphics driver, and complete the installation. Restart if prompted.
⮞ Windows 7
In Windows 7, open Start Menu → Control Panel → System and Security → Windows Update, click Check for updates, then go to Optional updates and install the available GPU driver. Since Windows 7 is a legacy operating system, driver availability may be limited; if no update appears, downloading the driver directly from the manufacturer’s website is recommended.
Update GPU Drivers from Official Manufacturers
Updating GPU drivers directly from official manufacturer websites ensures that the drivers are built specifically for the underlying GPU architecture and validated through hardware testing.
These drivers are developed in alignment with modern graphics frameworks such as Microsoft DirectX, OpenGL, and Vulkan, allowing the GPU to interact efficiently with both the operating system and graphics applications.
Official drivers often include targeted optimizations for newly released games, professional creative software, and evolving display technologies.
How to Update AMD GPU Drivers?
Steps:
How to Update NVIDIA GPU Drivers?
Steps:
How to Update Intel GPU Drivers?
Steps:
How to Back Up and Restore GPU Drivers?
GPU drivers come with built-in backup and restore options that can be used as a safety measure before updating the driver. If a new GPU driver does not work properly with the system, you can easily return to the previous stable driver using restore or rollback options.
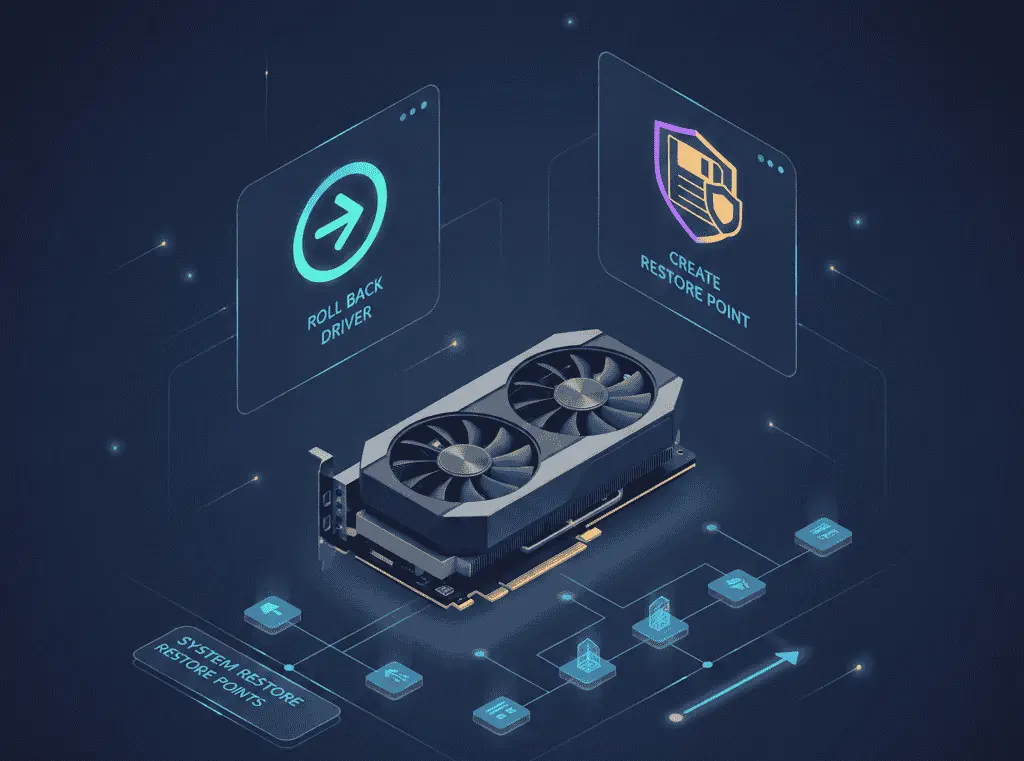

The most common way to restore a GPU driver in Windows is the “Roll Back Driver” option in Device Manager. If display issues, game crashes, or performance drops occur after a driver update, Windows allows you to revert to the previously installed driver version. This process only restores the driver files and does not affect system data or installed applications.
Driver backup is also indirectly handled through “System Restore Points”. When Windows installs updates or drivers, it often creates a restore point automatically. If the system becomes unstable after a GPU driver update, restoring the system to an earlier restore point will also bring the graphics driver back to a working state.
Conclusion
Keeping updated GPU drivers is essential for maintaining system stability, visual quality, and overall performance. Outdated or incompatible drivers can lead to rendering issues, game crashes, and poor compatibility with modern applications. Windows provides reliable built-in options such as Device Manager and Windows Update for basic and stable driver updates, while official manufacturer websites from NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel offer the most optimized drivers with access to advanced GPU features and performance improvements.